前言
我现在在做的项目有这样一个需求,从二进制文件反序列化出一个类(HeroDataRes),这个类里包含一个英雄的所有基本信息,然后服务端缓存这个类,等到玩家第一次请求的时候就新建一个运行时HeroDataRT类,并将数据传输过去,由于项目采用的状态同步策略,所以服务端需要持有每个玩家操控的英雄基本信息。基本关系就是这样
例子
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 using System;using System.Collections.Generic;namespace ConsoleApp1 { class Program { static void Main (string [] args { TestSupportor a = new TestSupportor(); a.StartTest(); } } public class TestSupportor { public Dictionary<int , object > FirstDic = new Dictionary<int , object >(); public Dictionary<int , object > CloneFirstDic; public Dictionary<int , int > SecondDic = new Dictionary<int , int >(); public Dictionary<int , int > CloneSecondDic; public void StartTest () { TestA a = new TestA(); FirstDic.Add(1 , a); Console.WriteLine($"字典A的成员值为{((TestA) FirstDic[1 ]).TestAInt} " ); CloneFirstDic = new Dictionary<int , object >(FirstDic); ((TestA) CloneFirstDic[1 ]).TestAInt = 2 ; Console.WriteLine($"字典A的成员值为{((TestA) FirstDic[1 ]).TestAInt} " ); Console.WriteLine($"字典B的成员值为{((TestA) CloneFirstDic[1 ]).TestAInt} " ); } } public class TestA { public int TestAInt = 1 ; } }
此时输出为 字典A的成员值为1 字典A的成员值为2 字典B的成员值为2 注释部分大家可以自行进行测试,最后我们可以得出,字典内部成员值是引用类型,那就是传递的引用地址,值是值类型,就是传递的值 显然,这会让我们项目一团糟,解决办法就是HeroDataRT赋值时,细化到每一个值引用,从而避免指向同一块内存 就像这样
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 using System;using System.Collections.Generic;namespace ConsoleApp1 { class Program { static void Main (string [] args { TestSupportor a = new TestSupportor(); a.StartTest(); } } public class TestSupportor { public Dictionary<int , object > FirstDic = new Dictionary<int , object >(); public Dictionary<int , object > CloneFirstDic; public void StartTest () { TestA a = new TestA(); FirstDic.Add(1 , a); Console.WriteLine($"字典A的成员值为{((TestA) FirstDic[1 ]).TestAInt} " ); CloneFirstDic = new Dictionary<int , object >(); TestA b = new TestA(); b.TestAInt = ((TestA) FirstDic[1 ]).TestAInt; CloneFirstDic.Add(1 ,b); ((TestA) CloneFirstDic[1 ]).TestAInt = 2 ; Console.WriteLine($"字典A的成员值为{((TestA) FirstDic[1 ]).TestAInt} " ); Console.WriteLine($"字典B的成员值为{((TestA) CloneFirstDic[1 ]).TestAInt} " ); } } public class TestA { public int TestAInt = 1 ; } }
运行结果 字典A的成员值为1 字典A的成员值为1 字典B的成员值为2
浅复制和深复制
对于上面提到的赋值问题,其实C#提供了一种解决方案,那就是继承ICloneable自己实现Clone函数 对于浅复制:值类型成员是分配在堆上的新实例,但是引用类型成员还是指向的原本的成员地址 对于深复制:值类型成员和引用类型成员都是分配在堆上的新实例
深复制的反序列化实现
转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/u013986317/article/details/85158633
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 public static T DeepCopy <T >(this T obj where T : class { try { if (obj == null ) { return null ; } BinaryFormatter binaryFormatter = new BinaryFormatter(); using (MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream()) { binaryFormatter.Serialize(stream, obj); stream.Position = 0 ; return (T) binaryFormatter.Deserialize(stream); } } catch { return null ; } }
使用方法:对象直接调用即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 [Serializable ] public class TestA { public int TestAInt = 1 ; } TestA a = new TestA(); TestB b = a.DeepCopy();
C#的计划支持
https://github.com/dotnet/csharplang/blob/master/proposals/recordsv2.md?tdsourcetag=s_pcqq_aiomsg
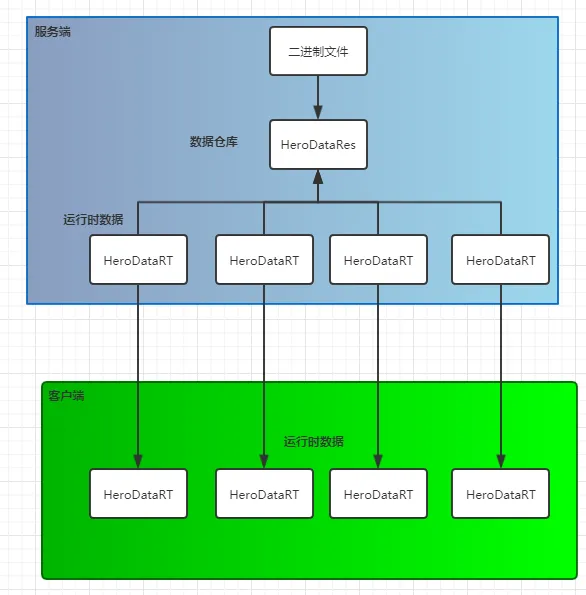 那么现在就要面临一个问题,HeroDataRT是从HeroDataRes取得的数据,而HeroDataRes里面难免会有class,我们都知道,字典本身是引用类型的,那么修改HeroDataRT类中的数据会不会对HeroDataRes里面的数据产生影响呢?
那么现在就要面临一个问题,HeroDataRT是从HeroDataRes取得的数据,而HeroDataRes里面难免会有class,我们都知道,字典本身是引用类型的,那么修改HeroDataRT类中的数据会不会对HeroDataRes里面的数据产生影响呢?